Benzene is a fundamental petrochemical building block used in the production of numerous chemical intermediates and end products, such as plastics, resins, synthetic fibers, rubber, dyes, detergents, and pharmaceuticals. As a volatile commodity, the benzene price trend analysis is influenced by a myriad of factors including crude oil prices, supply and demand dynamics, production capacities, geopolitical events, and environmental regulations. This article provides a detailed analysis of the historical and recent price trends of benzene, exploring the various factors driving these trends and offering insights into the future outlook for the benzene market.
Historical Price Trends
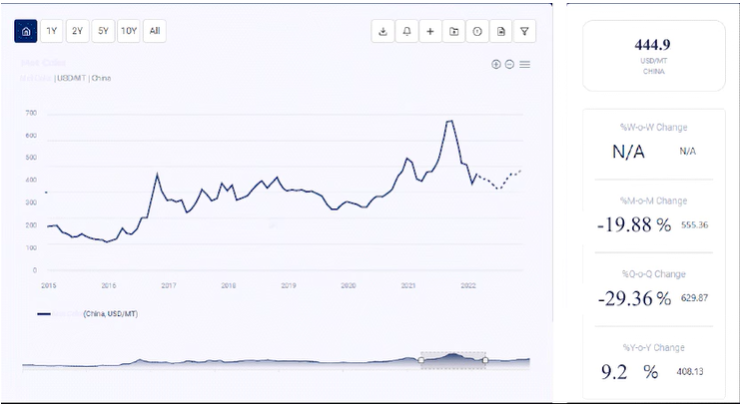
The price of benzene has seen significant fluctuations over the past few decades, reflecting changes in the global economy, crude oil prices, and the balance of supply and demand in the petrochemical industry.
-
During this period, benzene prices were relatively stable, closely tied to the prices of crude oil and other feedstocks like naphtha. Demand for benzene derivatives such as styrene and phenol drove steady consumption, while supply was maintained by robust production capacities in major producing regions like North America, Europe, and Asia.
-
Benzene prices experienced volatility during this time, influenced by sharp fluctuations in crude oil prices. The mid-2000s saw significant increases in crude oil prices, which pushed up the cost of benzene. The global financial crisis of 2008 led to a sharp decline in industrial activity and demand for benzene derivatives, causing a temporary drop in benzene prices. However, as economies began to recover, benzene prices rebounded in line with rising crude oil prices.
-
Benzene prices experienced relative stability with moderate fluctuations during these years. This period was characterized by steady demand from the automotive and construction sectors, which drove consumption of benzene derivatives like styrene. However, the market saw occasional price spikes due to supply disruptions and changes in crude oil prices.
-
A significant decline in crude oil prices during this period, driven by an oversupply in the oil market and decisions by OPEC to maintain high production levels, led to a corresponding drop in benzene prices. Lower feedstock costs for benzene production contributed to the decrease in prices.
-
Benzene prices saw a gradual increase as crude oil prices recovered from their lows. Increased production capacity in key regions, coupled with steady demand from the petrochemical industry, supported price stabilization. However, environmental regulations and shifts in production capacities occasionally caused price fluctuations.
-
The COVID-19 pandemic brought unprecedented disruptions to global markets, including the benzene market. Initial lockdowns led to a sharp decline in industrial activity and demand for benzene derivatives, causing prices to plummet. However, as economies began to recover and industrial activities resumed, the demand for benzene rebounded, leading to price volatility.
-
Post-pandemic recovery, coupled with geopolitical tensions such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, impacted crude oil prices and, consequently, benzene prices. Supply chain disruptions, increased production costs, and inflationary pressures contributed to higher benzene prices.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/benzene-price-trends/pricerequest
Key Factors Influencing Benzene Prices
Understanding benzene price trends necessitates an analysis of several key factors that consistently impact the market:
-
Crude Oil Prices: Benzene is a by-product of both the refining process and the production of ethylene through steam cracking, making its price closely tied to crude oil prices. Fluctuations in crude oil prices due to geopolitical events, OPEC decisions, and global supply-demand dynamics directly affect benzene prices.
-
Supply and Demand Dynamics: The balance between the supply of benzene and its demand from various industries significantly impacts prices. Key end-use sectors include the automotive industry (for styrene production), construction (for phenol and styrene derivatives), and consumer goods. Changes in these industries’ production levels and consumption patterns influence benzene demand.
-
Production Capacities and Technological Advances: The availability and capacity of refineries and steam crackers to produce benzene affect supply levels. Technological advancements that improve yield or efficiency in benzene production can impact supply and prices. Additionally, investments in new production facilities or upgrades to existing ones can shift market dynamics.
-
Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations and policies aimed at reducing emissions and promoting sustainability can influence benzene production costs and availability. Compliance with these regulations often necessitates investments in cleaner technologies and processes, impacting production costs and prices.
-
Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and sanctions can disrupt the supply chains for crude oil and petrochemicals, including benzene. Stability in major producing regions is crucial for maintaining consistent supply and pricing.
-
Global Economic Conditions: Macroeconomic factors such as GDP growth, industrial output, inflation, and trade policies influence the demand for benzene. Economic downturns can reduce industrial activities and lower demand, affecting prices.
Recent Price Movements
Analyzing recent price movements provides insights into the current state of the benzene market and potential future trends.
-
COVID-19 Impact: The pandemic initially caused a sharp decline in demand for benzene and its derivatives as industrial activities slowed. Prices plummeted due to reduced consumption in key sectors. However, as economies began to recover, the demand for benzene rebounded, leading to significant price volatility.
-
Geopolitical Tensions: The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has significantly impacted crude oil and benzene prices. Russia is a major producer of crude oil, and disruptions in its supply have led to increased global oil prices. Sanctions and trade disruptions have further exacerbated supply constraints, driving up benzene prices.
-
Supply Chain Challenges: Ongoing supply chain issues, including transportation delays, raw material shortages, and increased logistics costs, have affected the availability and pricing of benzene. These challenges have led to higher production costs and price volatility.
-
Inflationary Pressures: Rising costs for inputs such as energy, labor, and transportation have increased production costs for benzene. These inflationary pressures have been passed on to market prices, contributing to the overall increase in benzene prices.
-
Demand Recovery: The post-pandemic economic recovery has driven increased demand for benzene derivatives, particularly in the automotive and construction sectors. This renewed demand has supported higher benzene prices, especially as supply remains constrained by geopolitical and supply chain factors.
Future Outlook
The future price trend of benzene will be shaped by several critical factors:
-
Crude Oil Market Dynamics: The stability and pricing of crude oil will continue to play a crucial role in determining benzene prices. Monitoring OPEC decisions, geopolitical developments, and global supply-demand balance will provide insights into future benzene price trends.
-
Technological Innovations: Advances in petrochemical production technologies and the development of more efficient processes will influence market dynamics. Investments in research and development can lead to cost-efficient production methods and improved product quality, affecting prices.
-
Environmental Regulations: The implementation of stricter environmental regulations will drive demand for cleaner and more sustainable production processes. Compliance with these regulations will necessitate the use of advanced technologies, impacting production costs and prices.
-
Economic Recovery and Industrial Activity: Continued economic recovery post-pandemic will influence industrial activities and demand for benzene derivatives. Growth in emerging markets, in particular, can drive increased demand for benzene, supporting higher prices.
-
Geopolitical Stability: The resolution or escalation of geopolitical tensions, particularly in key oil-producing regions, will have a significant impact on global crude oil and benzene supply and prices. Monitoring these developments is crucial for predicting future price trends.
-
Supply Chain Resilience: Enhancing supply chain resilience through diversification of supply sources, investments in logistics infrastructure, and strategic stockpiling can mitigate disruptions and stabilize prices. Producers and consumers must adopt strategies to navigate supply chain challenges.
Conclusion
The price trend of benzene is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including crude oil prices, supply and demand dynamics, production capacities, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and global economic conditions. Despite recent volatility driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions, the overall demand for benzene remains robust, driven by its essential role in the production of numerous chemical intermediates and end products.
Looking ahead, the future price trend of benzene will depend on the stability of crude oil markets, technological innovations in production processes, compliance with environmental regulations, and the resolution of geopolitical tensions. Additionally, trends in economic recovery, industrial activities, and supply chain resilience will play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics.
Stakeholders in the benzene market, including producers, traders, and industry players, must stay informed about these evolving factors and adopt strategies to navigate the challenges and opportunities in the market. By understanding the underlying drivers of benzene prices and anticipating future trends, they can make informed decisions and ensure sustainable growth in the benzene industry.